Airway Management: Anatomy
The overall goal in airway management is to maintain a patent airway to provide oxygenation and ventilation.
Anatomy
Intubation is traditionally achieved with direct laryngoscopy. The optimal patient position for intubation is called the “sniffing position” or flexion-extension position. This allows for a direct line of site to the larynx. The three main axes involved are the mouth, oropharynx, and trachea.
Figure 1: In the neutral position
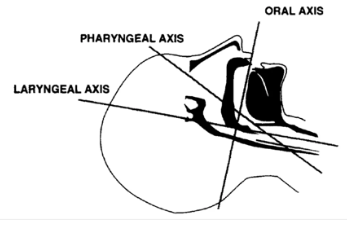
Figure 2: Extension of lower c-spine
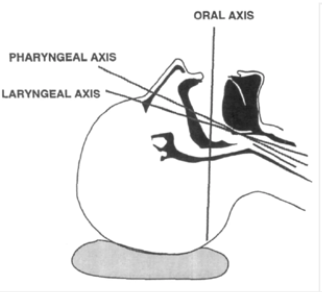
Figure 3: Extension at atlanto-occipital joint
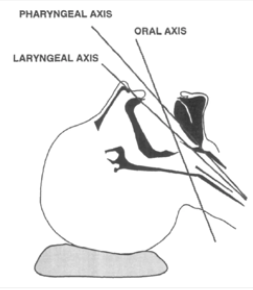
A laryngoscope or video laryngoscope should be inserted into the vallecular, the fold where the epiglottis meets the base of the tongue. The following structures can be seen on insertion of a laryngoscope or video laryngoscope.
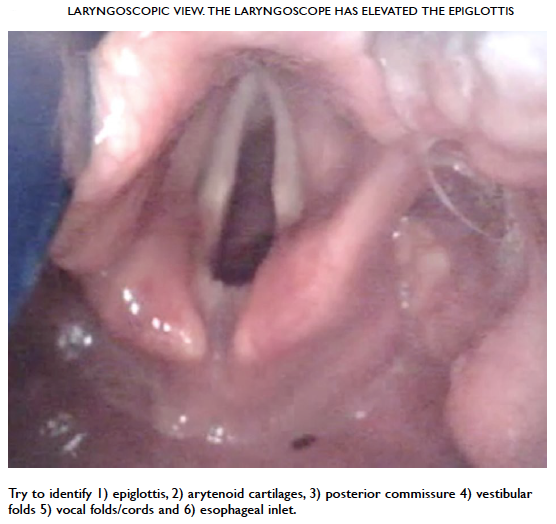
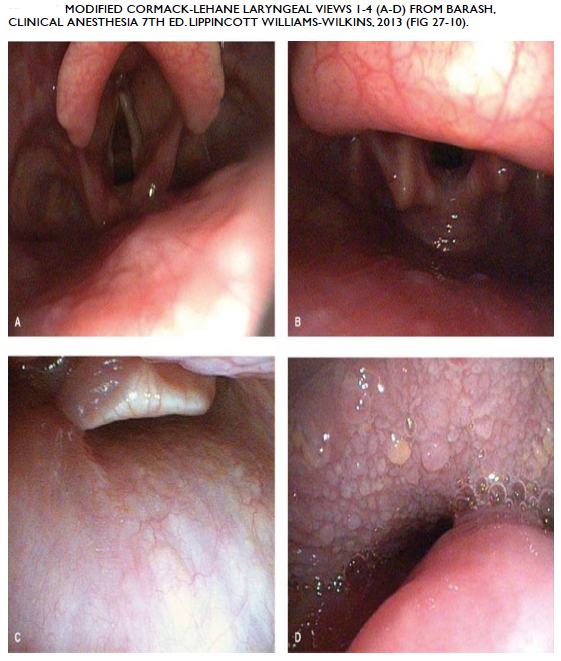
The modified Cormack-Lehane grading system classifies the view seen from laryngoscopy.
Next page: Options for Airway Management
