Regional Anesthesia: Anatomy
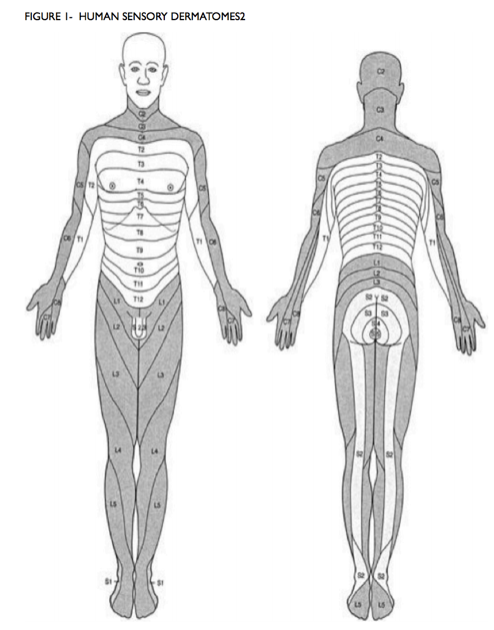
Dermatomes are areas of skin that are primarily supplied by one spinal nerve. Dermatomes are relevant for surgical anesthesia as which dermatomal levels need to be blocked for surgery depends on what kind of surgery is being performed. Figure 1 illustrates the different dermatomes of the body. Table 1 lists dermatomal levels needed for various surgical procedures.
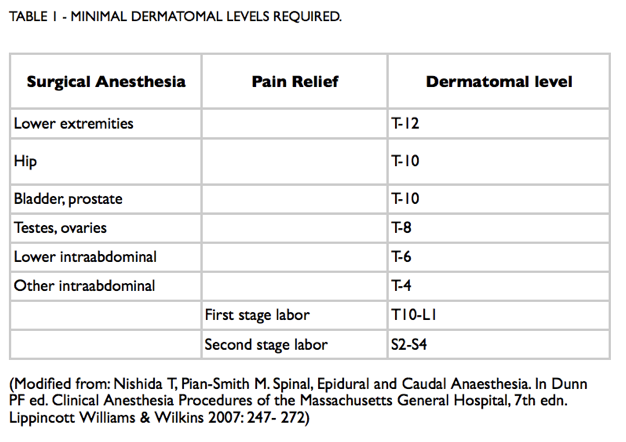
The spine has 33 vertebrae in total. There are 7 cervical, 12 thoracic, 5 lumbar, 5 fused sacral and 5 fused coccygeal vertebrae. The vertebrae encase the spinal cord, which typically ends at the level of L1. A pair of spinal nerves exits at each level. The cauda equine extends beyond the end of the spinal cord, and consists of all the spinal nerves L1.
The following structures are pierced during placement of a spinal needle into the subarachnoid space (Figure 2): skin, supraspinous ligament, interspinous ligament, ligamentum flavum, epidural space, dura and arachnoid membrane, and subarachnoid space.
Epidural anesthesia involves detecting epidural needle tip entry into the epidural space (just outside the dural sac) and passage of a fine catheter into the space. Unlike the case with spinal anesthesia, dural sac puncture with epidural needles, which are much larger in diameter, is usually unintentional. Epidural catheters permit intermittent injection or infusion of drugs over time during labor, for surgery and for postoperative pain relief.
Surface Landmarks
Surface landmarks can help to locate the desired level for needle insertion when proceeding with a spinal or epidural. Ultrasound can also be used to identify the desired level. (See Virtual Spine.)
Vertebrae
Surface Landmark
C7
First prominent spinous process in the back of neck
T7
At the level of the wing of the scapulae
L4/5
Level of the iliac crests (the line between these two bony prominences is Tuffier’s Line)
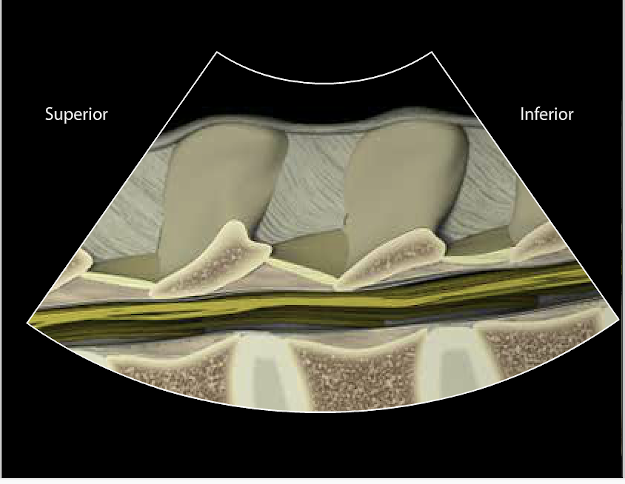
Image from: Virtual Spine.
Next page: Spinal and Epidural Blockade for Surgical Procedures
Previous page: Overview
