Obstetrical Anesthesia - Pain Management in Labour:
Stage of Labour
Etiology
Nerve supply
1
Contractions of lower segment of uterus and cervical dilatation
T10-L1
2
Vagina and perineum
S2-4
Non-Pharmacological Methods
Non-pharmacological methods include childbirth preparation (ex prenatal classes), emotional support, massage and touch therapy, therapeutic use of heat and cold, hydrotherapy, hypnosis, acupuncture, aromatherapy, and transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation.
Pharmacological Interventions
Method: Inhalational analgesia
Examples: Nitrous oxide
- Relatively contraindicated in pulmonary disease
Benefits: Quick to administer
Risks: Lack of scavenging system results in pollution
Method: Systemic analgesia
Examples: Opioids such as morphine, fentanyl IV PCA, remifentanil IV PCA
Benefits:
- Provides analgesia and anxiolysis
- Easy to administer
- High therapeutic ratio
- Relatively inexpensive
- Antidote available (Naloxone)
Risks:
- May cause maternal sedation and respiratory depression
- GI upset
- May cause hypotension
- Reduces fetal heart rate variability
- May cause neonatal respiratory depression and sedation
Method: Local Anesthesia
Examples:
- Infiltration of the perineum
- Paracervical block
- Pudendal nerve block
Benefits: Can provide excellent pain relief
Risks:
- Requires skilled personnel
- Paracervical block covers pain from contractions only; pudendal block covers pain from perineum only
Method: Regional Analgesia
Examples:
- Epidural
- Combined spinal-epidural (CSE)
Benefits:
- Awake patient
- Avoids airway manipulation
- Post-operative pain control
Risks: Discussed in further detail in sections below
Epidural Analgesia
Epidurals can be for analgesia in labor or anesthesia for C-Section. Epidural analgesia seeks to provide pain relief and minimize motor side effects. The dosages are unlikely to approach toxic levels as the concentrations are very dilute.
Indications include maternal request in active labour.
Contraindications include lack of patient consent, lack of proper equipment (including resuscitative equipment), lack of experienced personnel, infection at the site of puncture, septic shock, severe hypovolemia, severe coagulopathy or anticoagulation, supratentorial space occupying lesion.
Relative contraindications include mild coagulopathies, hemodynamic instability, stenotic valvular lesions, raised ICP, progressive neurologic deterioration of unknown etiology, spina bifida, severe scoliosis or previous back surgery, false labour.
Complications include infection (at skin or epidural abscess), bleeding (epidural hematoma), post-dural puncture headache, nerve damage, and failure (inadequate analgesia). Serious complications are rare. Epidural abscesses and hematomas may require surgical treatment. Nerve damage is usually managed expectantly with observation. In the event of hypotension or fetal bradycardia after initiating medications through the epidural catheter, the mother should be resuscitated with left uterine tilt, fluids, and a decrease in or discontinuation of epidural medications.
An epidural is typically “loaded” with local anesthetic (bupivacaine or ropivicaine usually) and then maintained with a continuous infusion of dilute local anesthetics, with patient-controlled epidural analgesia bolus, or a combination of both.
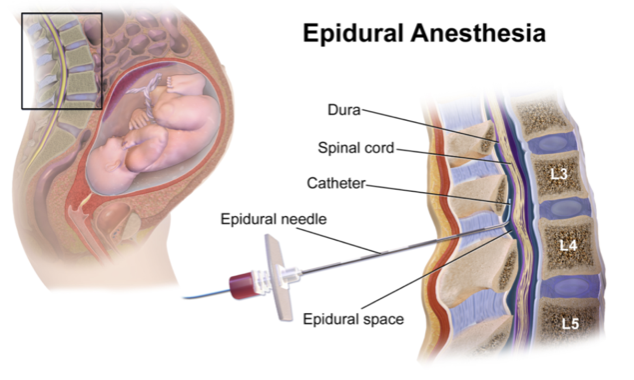
From WikiCommons
Combined Spinal Epidural (CSE)
The epidural space is identified in the standard fashion, a small gauge (25 or 27) non-cutting spinal needle is then passed through the epidural needle into the subarachnoid space with a small dose of bupivacaine 1-2mg +/- lipophilic opioid. The spinal needle is removed and an epidural catheter is placed for maintenance of analgesia. CSE allow for rapid onset of analgesia with little motor block. The disadvantage is the theoretical risk of 1) piercing the dura and possibly increasing the risk of infection or nerve damage and 2) a somewhat higher incidence of fetal heart rate abnormalities
