Airway Management: Rapid Sequence Induction
Airway reflexes that protect against aspiration are lost when a patient is induced or paralyzed for anesthesia. This increases the risk for aspiration of gastric contents. A rapid sequence induction (RSI) is a technique that minimizes the time between induction and intubation. For patients at increased risk for aspiration, see chapter on preoperative assessment. A thorough check of equipment should be completed before attempting airway intervention at any time, especially in the case of an RSI.
Technique:
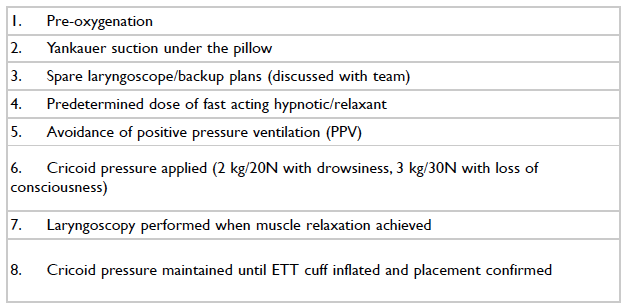
Note: The application of cricoid pressure is controversial and may result in more difficult intubation. If this is the case, the pressure can be removed to facilitate intubation.
Key features of a RSI is the avoidance of bag mask ventilation and precalculated drug dosages.
Next page: Extubation Criteria
Previous page: Difficult Airway Algorithm
